In an age where dietary choices significantly impact our well-being and the environment, the term “plant-based diet” has emerged as a symbol of health and environmental care. So, what exactly is a plant-based diet, and why is it so popular? In this brief introduction, we’ll explain the essence of a plant-based diet and delve into the reasons behind its growing appeal among those who want to take care of themselves and the planet.
Defining a Plant-Based Diet
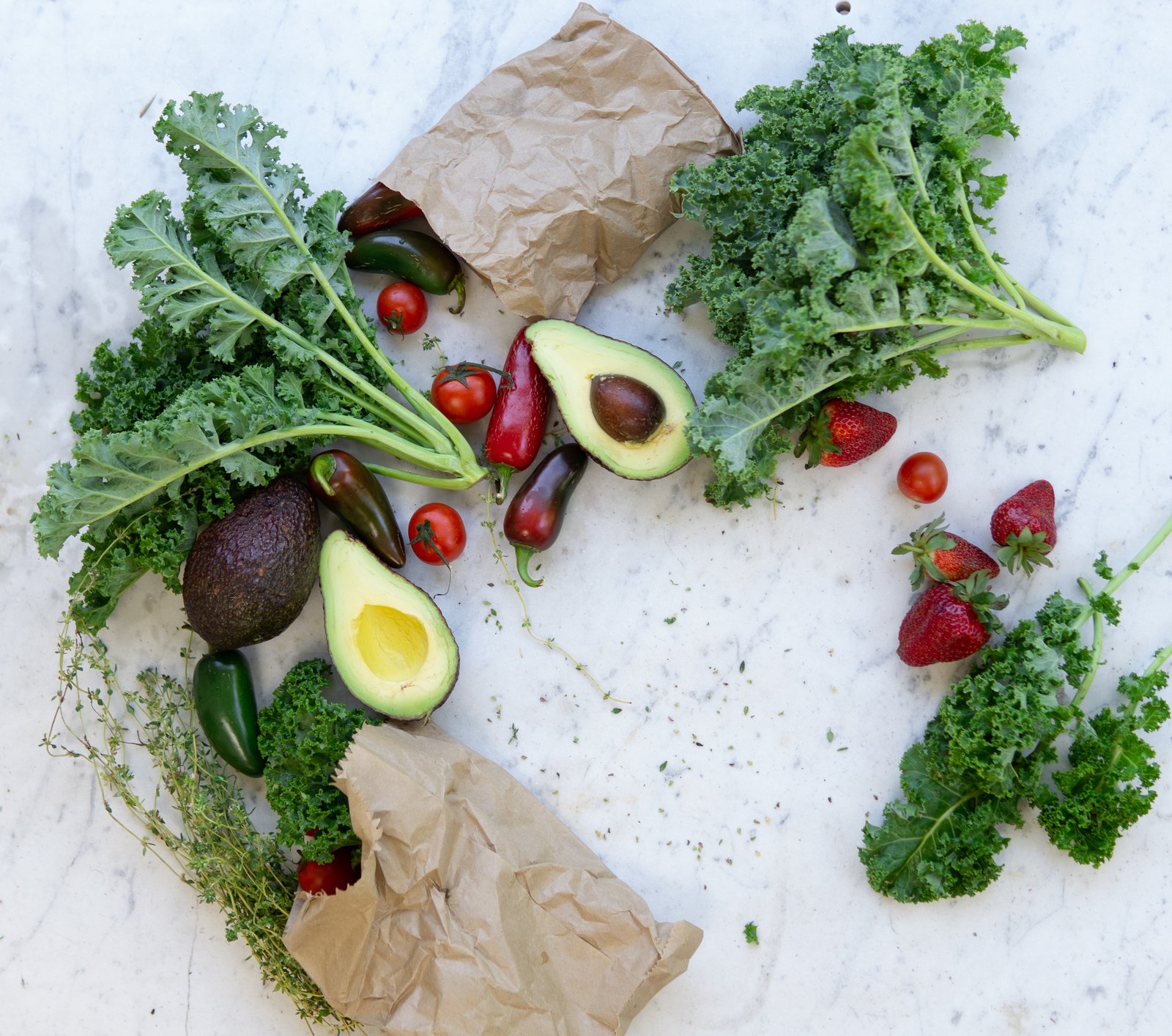
A plant-based diet is a dietary approach that emphasizes foods primarily derived from plants while minimizing or excluding animal products. The key components of a plant-based diet include:
- Fruits and Vegetables: These form the foundation of a plant-based diet. They provide essential vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants.
- Whole Grains: Whole grains like brown rice, quinoa, and whole wheat are rich in fiber and nutrients.
- Legumes: Beans, lentils, and peas are excellent sources of plant-based protein and fiber.
- Nuts and Seeds: These provide healthy fats, protein, and various micronutrients.
- Plant-Based Proteins: Tofu, tempeh, and seitan are protein-rich options that can be used as meat substitutes.
- Plant Oils: Olive oil, avocado oil, and other plant oils are preferred sources of fats.
How Is It Different from Vegetarian or Vegan Diets?
- Vegetarian Diet: A vegetarian diet excludes meat, poultry, and seafood but may still include animal-derived products like dairy and eggs.
- Vegan Diet: A vegan diet excludes all animal products, including meat, dairy, eggs, and even honey.
- Plant-Based Diet: While it can overlap with vegetarian and vegan diets, a plant-based diet primarily focuses on whole, plant foods but may occasionally include small amounts of animal products or processed foods.
The Health Benefits:
A well-balanced plant-based diet offers several health benefits:
- Heart Health: A lower intake of saturated fats and cholesterol can reduce the risk of heart disease.
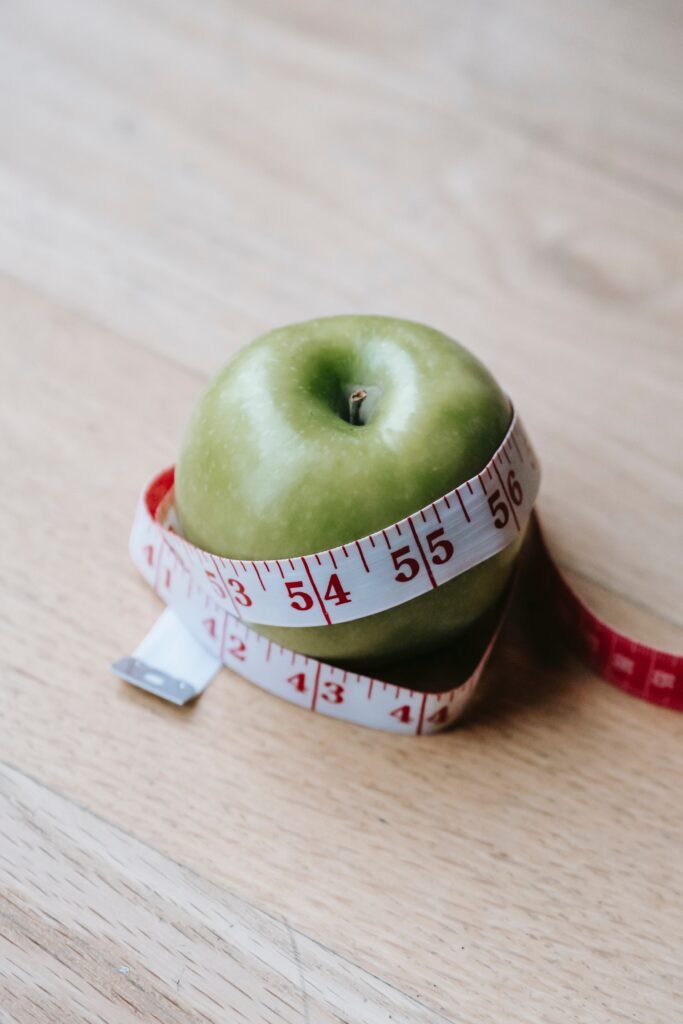
- Weight Management: Plant-based diets support weight management due to their lower calorie density and higher fiber content, which helps promote feelings of fullness.
- Lower Risk of Chronic Diseases: Research suggests that plant-based diets may reduce the risk of type 2 diabetes, certain cancers, and hypertension. The abundance of antioxidants and phytochemicals in plant foods contributes to these protective effects.
- Digestive Health: The fiber-rich nature of plant-based diets promotes a healthy digestive system, reducing the risk of constipation and supporting gut health.
Environmental Considerations
Beyond individual health, plant-based diets have gained attention for their positive impact on the environment.
- Reduced Carbon Footprint: Plant-based diets typically have a lower carbon footprint compared to diets rich in animal products. Producing plant foods generates fewer greenhouse gas emissions and requires less land and water.
- Conservation of Resources: By reducing meat and dairy consumption, we can preserve vital resources like water and land, helping to combat deforestation and habitat destruction.
- Ethical and Sustainable Choices: Choosing plant-based foods aligns with principles of animal welfare and ethical treatment, as well as promoting sustainable agricultural practices.
How to Adopt a Plant-Based Diet:
Transitioning to a plant-based diet can be gradual. Here are some practical tips:
- Gradual Shift: Start by incorporating more fruits, vegetables, and plant-based protein sources into your meals while reducing animal products over time.
- Diverse Foods: Explore a wide variety of plant-based foods to ensure you get a broad spectrum of nutrients. Experiment with different grains, legumes, nuts, and seeds.
- Meal Planning: Plan your meals to ensure you meet your nutritional needs. Include foods rich in protein (e.g., tofu, beans), healthy fats (e.g., avocados, nuts), and essential nutrients (e.g., B12, iron).
- Seek Guidance: Consult with a healthcare professional or nutritionist to address any specific dietary concerns or nutritional requirements.
IIn brief, a plant-based diet centers on plant-derived foods while reducing or eliminating animal products. It brings about numerous benefits, including improved heart health, effective weight management, and a lowered risk of chronic diseases. Moreover, it aligns with environmental sustainability and ethical values by reducing carbon emissions and conserving resources. Whether driven by health, environmental consciousness, or ethical considerations, adopting a plant-based diet is a meaningful and impactful choice that promotes well-being for individuals and the planet.
The Power of Plant-Based Diets in Weight Loss